An Intro to Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a complete medical system that has been used to diagnose, treat, and prevent illnesses for more than 2,000 years. Its basic concept is that a vital force of life, called Qi, surges through the body, and any imbalance to Qi can cause disease and illness. TCM practitioners use treatments that are specific to the individual, such as acupuncture, cupping, or moxibustion, to restore this balance. In this blog, we will explore the great practitioners of TCM, along with Qi and the meridians of the body, and TCM’s use in herbal medicine, food, genetics research, and drug development.
A Look At Traditional Chinese Medicine
China has one of the world’s oldest medical systems with acupuncture and Chinese herbal remedies dating back at least 2,200 years. The earliest known written record of Chinese medicine is the Huangdi Neijing (The Yellow Emperor’s Inner Classic) from the 3rd century BCE, which provided the theoretical concepts for TCM that remain the basis of its practice today.
In essence, TCM healers seek to restore a dynamic balance between two complementary forces, Yin (passive) and Yang (active), which pervade the human body as they do the universe as a whole. According to TCM, a person is healthy when harmony exists between these two forces; illness, on the other hand, results from a breakdown in the equilibrium of Yin and Yang.
Treatments to regain a Yin and Yang balance may include:
- Acupuncture, which involves the insertion of very thin needles through the skin at strategic points on the body.
- Moxibustion, which consists of burning dried mugwort on particular points on the body.
- Cupping, which is a form of alternative medicine in which a local suction is created on the skin with the application of heated cups.
- Massage, which can help to regulate the flow of energy and blood, increase blood circulation, and relieve body pain and stress.
- Herbal remedies, which can strengthen organ function and support good health.
- Movement and concentration exercises, such as tai chi, which include specifically-designed movements to help an individual regain balance.
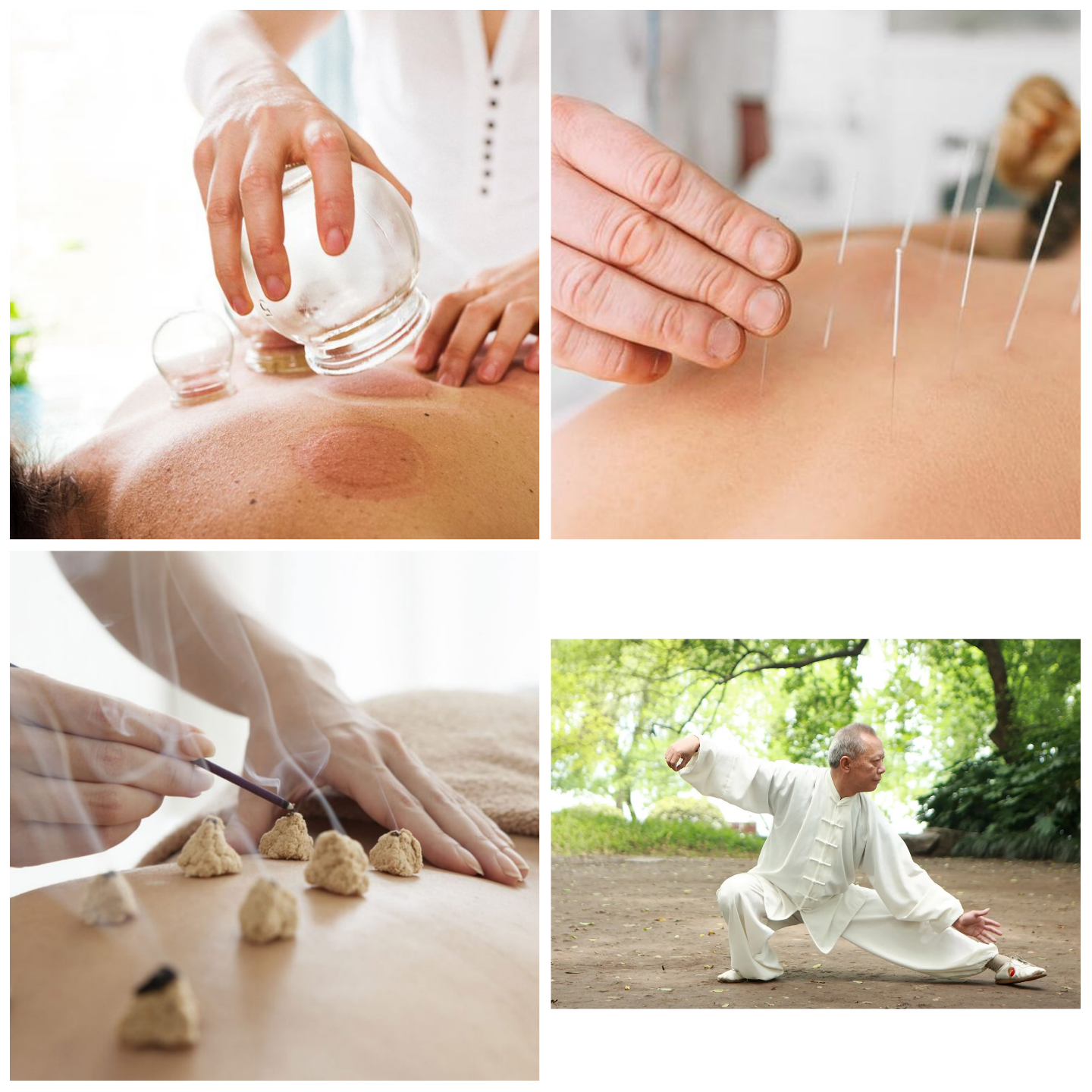 Pictured: Cupping; top left (The Thirty), Acupuncture; top right (Forbes), Moxibustion; bottom left (American institute of Alternative Medicine), Tai Chi; bottom right (Britannica)
Pictured: Cupping; top left (The Thirty), Acupuncture; top right (Forbes), Moxibustion; bottom left (American institute of Alternative Medicine), Tai Chi; bottom right (Britannica)
The Great Practitioners of Traditional Chinese Medicine
The hard work and dedication of various practitioners in ancient China have made an impact on not just Traditional Chinese Medicine, but also Western Medicine. A few great practitioners of TCM to take note of are:
Zhang Zhongjing
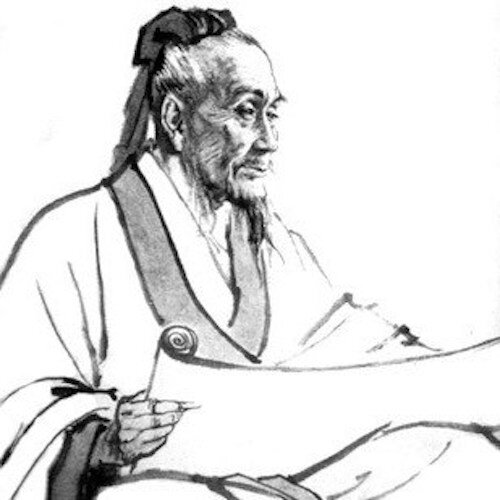

Pictured: Zhang Zhongjing Source: The Wandering Cloud ACM
Zhang Zhongjing (150-219 CE), the most famous of China’s physicians, lived during the Eastern Han dynasty and was known for his remarkable medical skill and significant contribution to Traditional Chinese Medicine. He wrote a medical masterpiece entitled Shanghan Lun (Treatise on Cold Damage Diseases). Zhang Zhongjing’s theory and prescriptions, such as moxibustion, acupuncture, and herbal medicine, are still of great medical value and are the standard reference work for TCM.
Hua Tuo
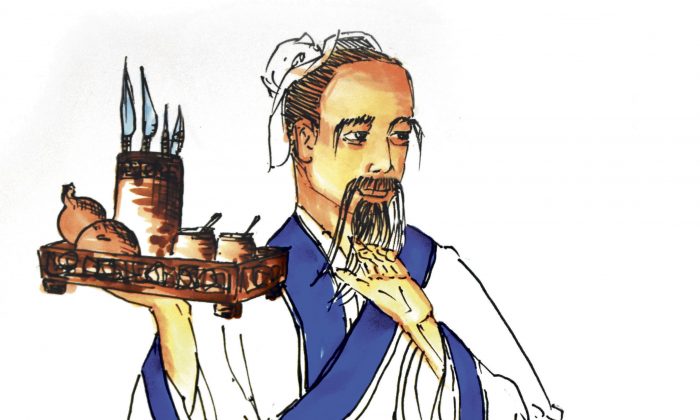

Pictured: Hua Tuo Source: The Epoch Times
Another famous physician of Traditional Chinese Medicine was Hua Tuo (145-208 CE). Hua Tuo developed the use of anesthesia in surgery and further advanced the Chinese’s knowledge of anatomy. He was also the first person to use narcotic drugs in the world, preceding the West by about 1600 to 1700 years.1
Wang Shuhe

Pictured: Wang Shuhe Source: The Coltons Point Times
Wang Shuhe (180-270 CE) was a Chinese physician who wrote the Maijing (The Pulse Classics), which is an influential work describing the pulse and its importance in the diagnosis of disease. Wang Shuhe’s contributions to medical science were not limited to sphygmology, though; he also made outstanding contributions to the collation of ancient literature.
Traditional Chinese Medicine, Qi, and the Meridians
A main aspect of TCM is an understanding of the body’s Qi, which is known as life force and literally translates to “vital breath.” Qi is universal and embraces all manifestations of energy, from the most material aspects of energy, such as the earth beneath your feet, to the most immaterial aspects, such as light and emotion.
Life, it’s said in the Chinese medical classics, is a gathering of Qi. A healthy and happy human being is a dynamic but harmonious mixture of all the aspects of Qi that make up who we are. Qi is in a state of continuous flux, transforming endlessly from one aspect of Qi into another. It’s neither created nor is it ever destroyed; it simply changes in its manifestation.2
Qi flows through invisible meridians, or channels, of the body that connects organs, tissues, veins, nerves, cells, atoms, and consciousness itself. There are 12 major meridians with each connecting to one of the 12 major organs in TCM theory. The meridians are also related to circadian rhythms, seasons, and planetary movements, which create additional invisible networks.
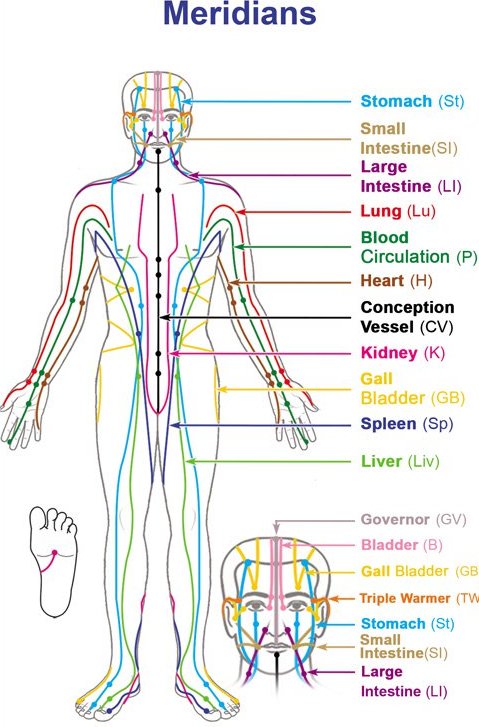
Pictured: The Meridians Source: Dr. Huong
In acupuncture, for example, very thin needles are inserted into specific areas along the meridians. The needles stimulate the meridians and readjust the flow of Qi to balance the body’s Yin and Yang. While the meridian network can be used to alleviate symptoms, it’s also said that TCM can endow individuals with the ability to change consciousness after treatments.
To learn more about Qi, the meridians, and acupuncture, click here.
Traditional Chinese Medicine’s Five Element Theory
Philosophers have questioned the origins of life and the makeup of the universe since prehistory, the time before written records existed. According to some traditions, including TCM, everything in the universe comes from the five elements: wood, fire, earth, water, and metal.
“The five elements are used in pretty much every different style of TCM to some extent to diagnose and differentiate between different illnesses, dysfunctions, and people,” says Tiffany Cruikshank, licensed acupuncturist, experienced registered yoga teacher, and founder of Yoga Medicine.
The elements are all connected; wood feeds fire, fire makes earth, earth creates metal, metal holds water, and water nourishes wood. Each element both controls and is controlled by another element. One element may manifest heavier within us than others, which is where we are strongest, yet most vulnerable.
Each element has unique characteristics and becoming aware of your elemental dominance can help explain the physiology and pathology within your body. Here’s a breakdown of the five elemental types in TCM:
- A “Wood Personality” is someone who is athletic, energetic, and adventurous. Wood personalities tend to be anxious and angry, and may suffer from orthopedic issues, migraines, or ADD.
- A “Fire Personality” is someone who is passionate, creative, and authoritative. Fire personalities tend to be impulsive and irritable, and may suffer from insomnia, high blood pressure, chest pains, or headaches.
- An “Earth Personality” is someone who is nurturing, generous, and caregiving. Earth personalities tend to be worrisome and pensive, and may suffer from abdominal issues or hormonal problems.
- A “Metal Personality” is someone who is meticulous, honest, and responsible. Metal personalities tend to be melancholy and may suffer from constipation, lung and skin issues, or allergies.
- A “Water Personality” is an old soul that is known to be wise, reflective, and private. Water personalities tend to be indecisive, fearful, and paranoid, and may suffer from back pain, knee pain, and kidney and bladder infections.
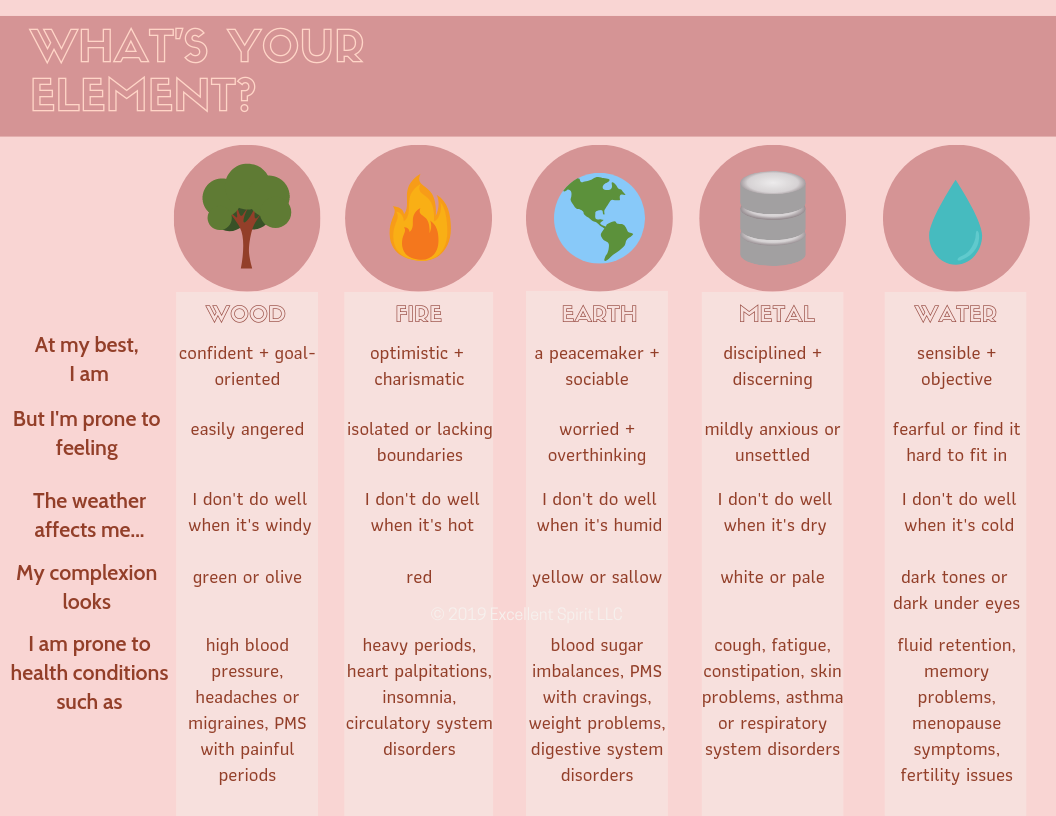 Pictured: The Five Element Theory traits and characteristics Source: Scottsdale Acupuncture
Pictured: The Five Element Theory traits and characteristics Source: Scottsdale Acupuncture
If you want to find out your element type, you can take this quiz.
Traditional Chinese Medicine and Herbal Therapy
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, herbs and herbal formulas are used to strengthen organ function and support good health. TCM practitioners have an understanding of the essence of various herbal components to create a healing effect that goes beyond the chemical composition and physical properties of the herbs to correctly stimulate or adjust the body’s own energy vibration.
Many TCM herbal formulas have been in use for more than 2,200 years, and are composed of ingredients chosen to function in combination with each other. In Western Medicine, medications are commonly prescribed for a specific effect, while in TCM, each herb in a formula has a different purpose or role to help the body achieve harmony.
For a plant to be included in TCM herbal therapy, each of its parts has to be identified for a different healing purpose. The following are a few of the most used Traditional Chinese Medicinal herbs, along with their benefits:
- Ginkgo Biloba: Promotes Brain Health and Improved Memory
- Ginseng (Ren Shen): Offers Immune Support and Improved Bone Strength
- Turmeric: Possesses Anti-inflammatory, Anti-oxidant, and Digestive Health Properties
- Astragalus (Huang Qi): Offers Immune Support and Brain Protection
- Cinnamon: Regulates Blood Sugar and Promotes Dental Health
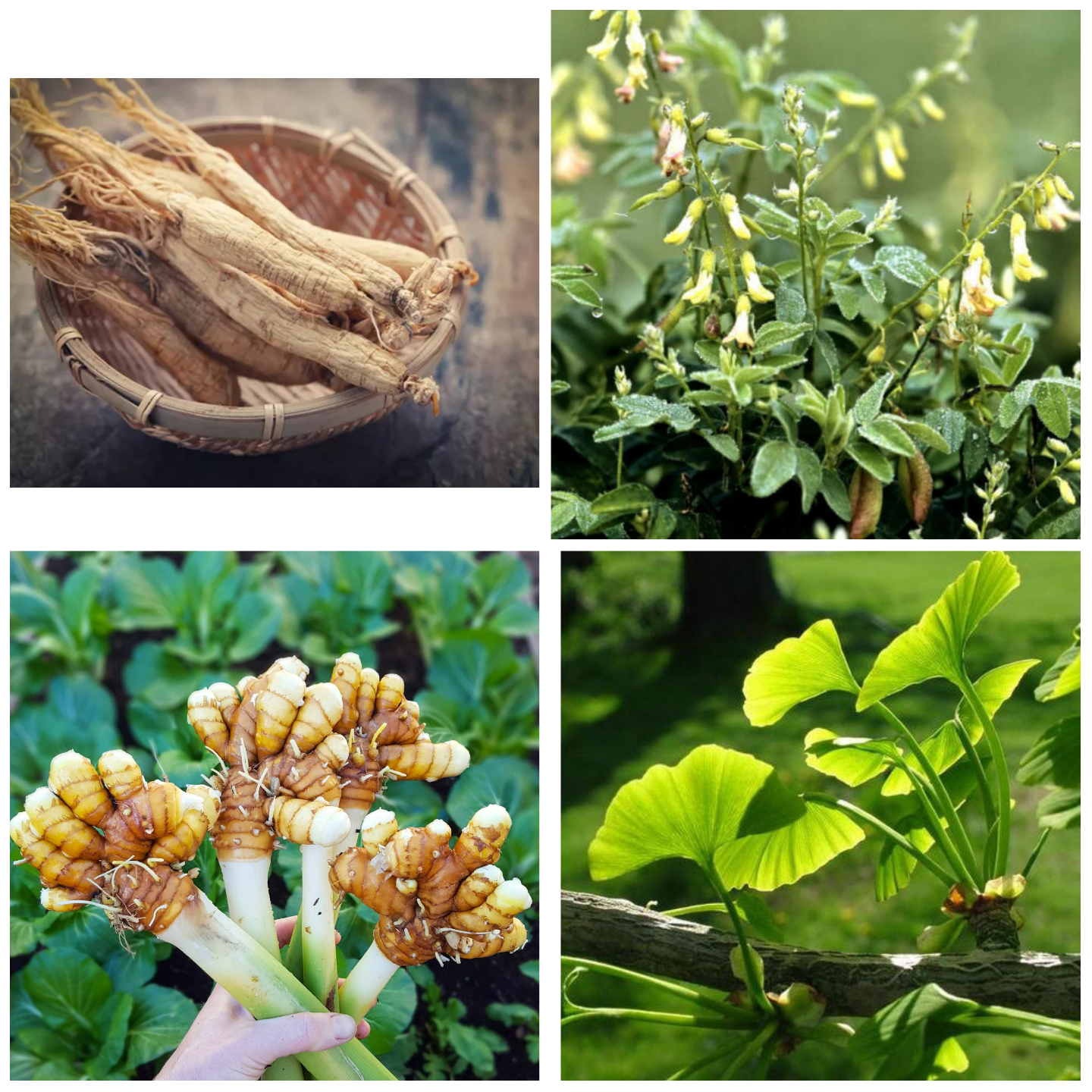

Pictured: Ginseng; top left (Me & Qi), Astragalus; top right (EBAY), Turmeric; bottom left (Homestead and Chill), Ginkgo Biloba; bottom right (Indiamart)
Herbs can have effects on the body as powerful as pharmaceutical drugs, which is why you should consult with your doctor before taking part in herbal therapy. Additionally, you should never abandon your regular medication or alter the dose without the knowledge and approval of your doctor.
Traditional Chinese Medicine and Food
Much like herbs, TCM views the healing properties of foods in the same way; different foods carry different energies that can go directly to specific organs to help them heal. Food is divided into five natures, called “siQi”: cold, cool, neutral, warm, and hot. The nature of food is not determined by its actual temperature, but rather by what effects it will have on an individual’s body after consumption.
According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, when a person continually eats one type of food, it creates an imbalance in their body and affects their immune system. Thus, one of the keys in Traditional Chinese Medicine is to keep our body “neutral.” Traditional Chinese Medicine also tells us that having food at a moderate temperature is ideal to avoid overstraining the digestive organs.3
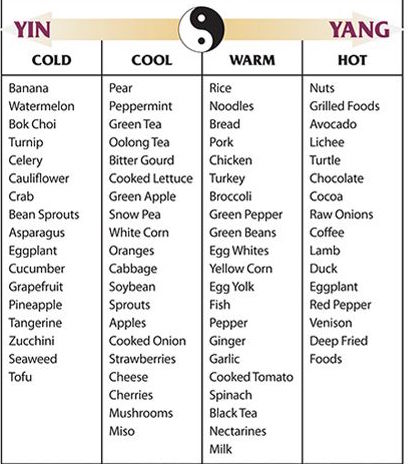
Pictured: Traditional Chinese Medicine Food Chart Source: Pinterest
There’s a saying in TCM: “The five grains provide nourishment. The five vegetables provide filling. The five domestic animals provide enrichment. The five fruits provide support.” This means that a balanced diet, where foods are consumed in appropriate combinations according to their natures and flavors, serves to supplement the essence that the human body needs.4
Traditional Chinese Medicine, Genetic Research, and Drug Development
Considering the fact that Traditional Chinese Medicine is now an academic discipline in the field of medicine, there are modern developments that are worth taking note of, such as the use of TCM in genetics research.
The Yin and Yang principle can be applied to a genetic disease such as inherited breast cancer and its associated genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. According to this principle of natural law, if either of these genes is activated, somewhere in another part of the genetic code there also exists a gene to fix this action. There must be complementary programs running — one for developing the disease and one for healing it.5
In addition to genetics research, nearly 200 modern medicines have been developed either directly or indirectly from the 7,300 species of plants used in TCM. For example, ephedrine, an alkaloid used to treat asthma, was first isolated from the Chinese herb Ma Huang. Another alkaloid known as huperzine A was isolated from a widely used ingredient in Traditional Chinese Medicine known as Huperzia serrata, which is a type of fir moss.
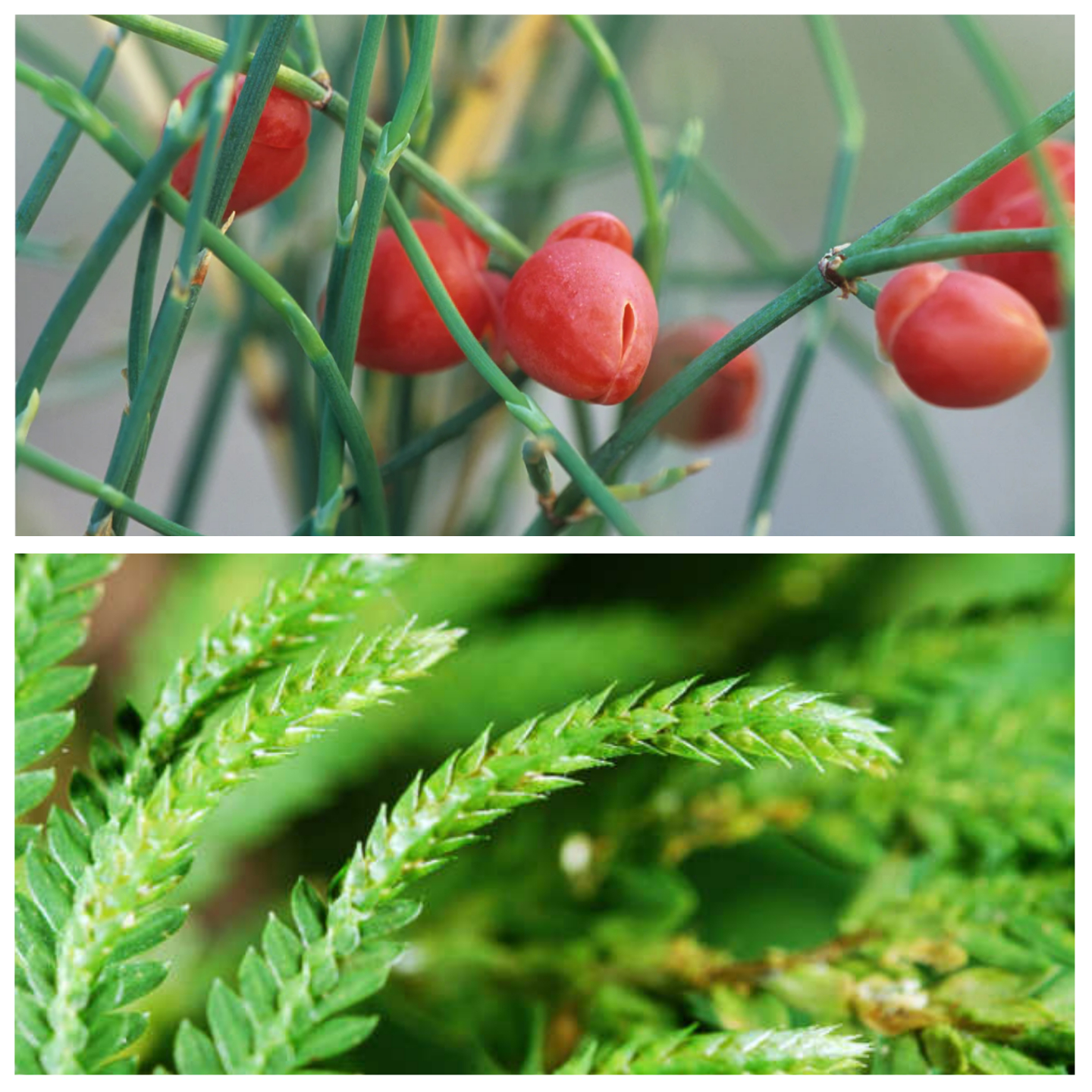 Pictured: Ma Huang; top (The Plant Attraction), Huperzia serrata, bottom (HSN)
Pictured: Ma Huang; top (The Plant Attraction), Huperzia serrata, bottom (HSN)
In Conclusion
Even if you aren’t familiar with all of the fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine, you’re probably familiar with some of its practices. Maybe you’ve had an acupuncture session, taken turmeric for arthritis pain, or signed up at the local tai chi studio. Either way, TCM’s popularity has remained consistent throughout the centuries for improving health and wellness when used alongside conventional medical therapies.
What is your TCM elemental type? Have you ever tried a TCM treatment? Let us know in the comments!
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hua_Tuo [1]
https://magazine.circledna.com/what-does-traditional-chinese-medicine-say-about-qi/ [2]
https://www.pingminghealth.com/article/581/warming-and-cooling-characteristics-of-common-foods/ [3]
https://qiblog.emperors.edu/2015/10/the-role-of-healthy-eating-in-traditional-chinese-medicine/ [4]
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3814386/ [5]